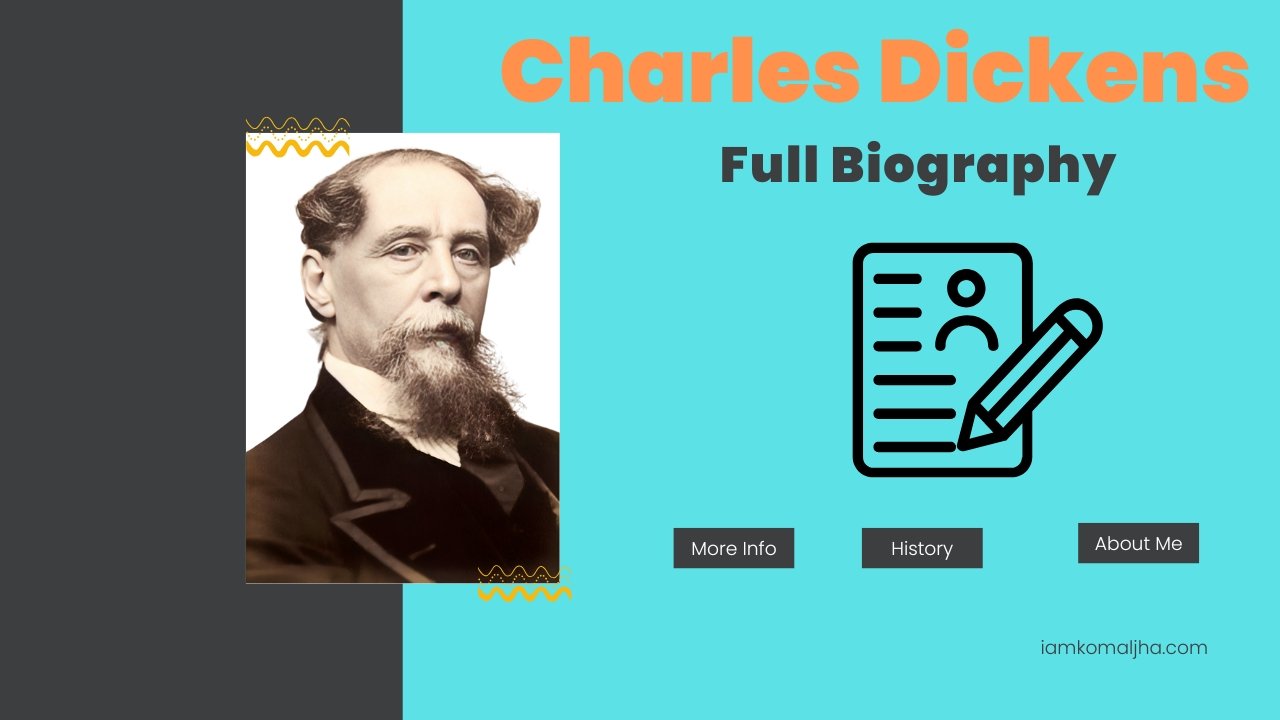
Charles Dickens Complete Biography: Charles Dickens, one of the most prominent writers of the Victorian era, left behind a legacy that continues to captivate readers worldwide. His novels, filled with complex characters, moral commentary, and rich storytelling, have made him a household name in the world of literature. This biography explores the life of Charles Dickens, his early years, his journey as a writer, his most significant works, and his lasting impact on society and literature.
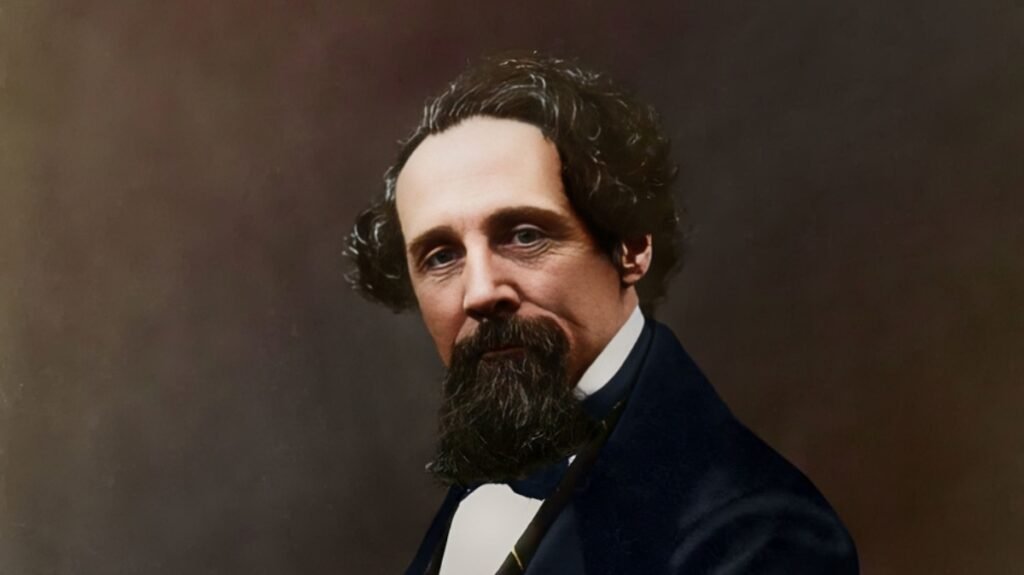

Charles Dickens Complete Biography
Charles Dickens Complete Biography: This biography explores the life of Charles Dickens, from his humble beginnings to his rise as a literary giant. It delves into his prolific writing career, highlighting his most famous works and their impact on readers around the world. It also touches upon his personal struggles, including his challenging childhood, complex family life, and commitment to social reform. Ultimately, Dickens’s legacy endures, as his stories continue to resonate with readers and inspire adaptations across various mediums.
Charles Dickens
| Full Name | Charles John Huffam Dickens |
| Birth | 7 February 1812 |
| Age at Death | 58 years old |
| Birthplace | Portsmouth, Hampshire, England |
Charles Dickens Early Life and Background
Charles Dickens Complete Biography: Charles Dickens was born on 7th February 1812 in Portsmouth, Hampshire, England, at 1 Mile End Terrace (now 393 Commercial Road). He was the second of eight children of John Dickens, a clerk in the Navy Pay Office, and Elizabeth Dickens (née Barrow). Dickens’s early life was marked by his father’s financial troubles, which ultimately led the family to experience poverty. When Charles was just two years old, his father was imprisoned for debt, forcing the Dickens family to move to London. At the age of twelve, Dickens was sent to work in a blacking factory, a traumatic experience that deeply influenced his later writings.
Charles Dickens Age and Birth
Charles Dickens Complete Biography: Born on 7th February 1812, Dickens was brought into the world during a time of great industrial transformation. His birthplace, Portsmouth, was rapidly changing due to the effects of industrialization, and Dickens’s early years were marked by hardship and struggle. This formative experience would later shape his views on the inequalities of society, which he frequently explored in his literary works.
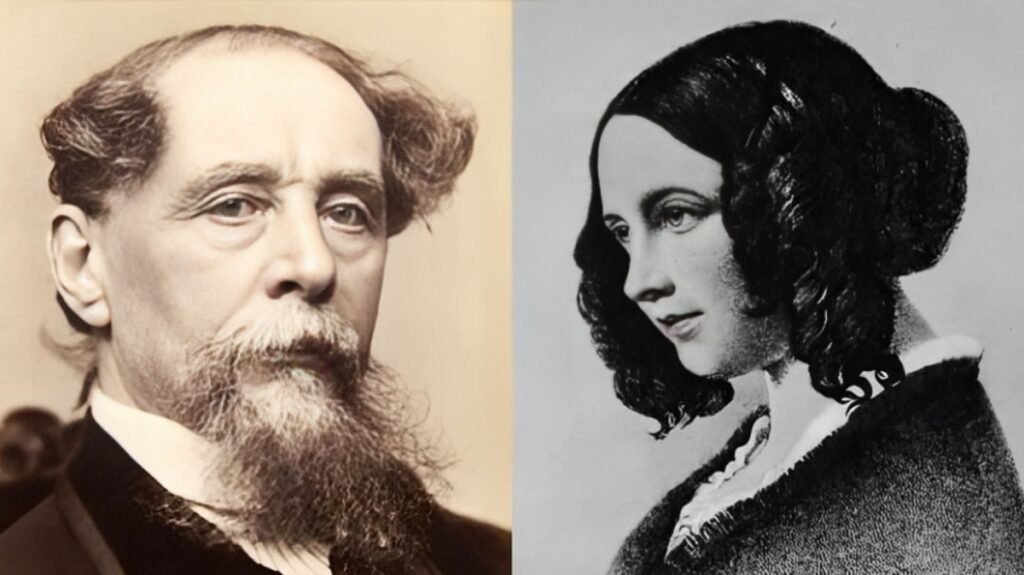

Charles Dickens Family
Charles Dickens Complete Biography: Charles Dickens came from a large family, being one of eight children. His father, John Dickens, was often unable to manage his finances, which led to periods of poverty for the Dickens family. Despite these difficulties, Dickens was very close to his family, particularly his mother, Elizabeth, who supported his education and personal development.
Dickens married Catherine Thomson Hogarth in 1836. The couple had ten children together, though their marriage eventually ended in separation in 1858. Dickens had a long-standing relationship with Ellen Ternan, a young actress, after his separation from Catherine.
Charles Dickens Wife and Children
Charles Dickens’s marriage to Catherine Thomson Hogarth lasted for over 20 years. The couple had ten children: Charles Dickens Jr., Mary Dickens, Kate Perugini, Walter Landor Dickens, Francis Dickens, Alfred D’Orsay Tennyson Dickens, Sydney Smith Haldimand Dickens, Henry Fielding Dickens, Dora Annie Dickens, and Edward Dickens. Though they shared a large family, Dickens’s personal life was marred by difficulties. He eventually separated from Catherine in 1858 and formed a relationship with Ellen Ternan, who was much younger than him.

Charles Dickens Career
Early Career and Writing Beginnings
Charles Dickens Complete Biography: Dickens’s career began in the world of journalism, where he worked as a reporter and editor. In the 1830s, he contributed to several periodicals, gaining recognition for his witty, satirical, and social commentary. In 1836, Dickens published Sketches by Boz, which marked the beginning of his illustrious career as a novelist.
His first major novel, Oliver Twist, was published in 1838, followed by Nicholas Nickleby in 1839. Dickens continued to write prolifically, releasing many other famous works, such as A Christmas Carol (1843), David Copperfield (1850), Bleak House (1853), and A Tale of Two Cities (1859). Dickens was known for publishing his novels in serial form, keeping readers eagerly anticipating the next chapter.
Charles Dickens Rise to Fame: Major Works
Charles Dickens rose to fame with The Pickwick Papers, his first serialized novel. However, it was Oliver Twist that cemented his place as a literary giant. His ability to blend social critique with compelling storytelling captivated readers of all classes. Dickens’s works often featured vivid characters, social commentary, and a keen sense of justice.
Other notable works include Great Expectations, Bleak House, and A Tale of Two Cities. Each novel depicted the struggles of the working class, the corrupt systems of the time, and the challenges of growing up in Victorian England. Dickens’s storytelling was highly influential, and his novels were often serialized to maximize their impact and ensure their accessibility to a wide audience.

Charles Dickens Net Worth
Charles Dickens Complete Biography: At the time of his death, Charles Dickens’s estimated net worth was significant. His literary success and popularity allowed him to live comfortably. Though exact figures are hard to determine, his wealth was largely amassed through the sales of his novels, public readings, and editorials. Dickens’s social status as an author and public figure also contributed to his financial success, and he was one of the highest-paid writers of his time.
Charles Dickens Education
Dickens’s formal education was inconsistent due to his family’s financial instability. He attended several schools, including Wellington House Academy and Mr. Dawson’s school, before being sent to work in a blacking factory at the age of twelve. Despite this, Dickens was largely self-educated, immersing himself in literature and expanding his knowledge through his love of reading. His lack of formal education did not hinder his literary success, and his self-taught knowledge and experiences shaped his writing style.
Charles Dickens Height
Charles Dickens Complete Biography: While exact measurements are difficult to come by, various reports and images suggest that Dickens was of average height for his time, around 5 feet 8 inches (173 cm). His energetic and expressive personality, however, made a much greater impression than his physical stature.

Charles Dickens Social Media
Though Charles Dickens lived in the 19th century, his literary fame and social critiques made him an early advocate for social justice. If Dickens were alive today, his social media presence would likely be filled with insightful commentary on societal issues, critiques of inequality, and perhaps even modern-day social justice movements. Dickens’s legacy lives on through the continued popularity of his works and the social changes they helped spark.
Charles Dickens Songs and Albums
Charles Dickens Complete Biography: Dickens did not write songs or albums, but his works have been adapted into countless musical productions, films, and television shows over the years. A Christmas Carol, perhaps his most famous work, has inspired many musicals, songs, and adaptations. His characters and stories continue to inspire artists and musicians today.
Charles Dickens Achievements
Dickens’s achievements were numerous and wide-ranging. Some of his most notable contributions include:
- The creation of iconic characters like Ebenezer Scrooge, Oliver Twist, and David Copperfield.
- Pioneering the serialized novel format, which allowed readers to engage with his stories in a new way.
- Social advocacy, including campaigning against child labor, poor working conditions, and the mistreatment of the poor.
- Popularizing Christmas through works like A Christmas Carol, which remains a central part of Christmas culture.
Charles Dickens Later Works and Legacy
Charles Dickens Complete Biography: In his later years, Dickens continued to write and campaign for social reforms. His works from the 1850s and 1860s, such as Little Dorrit (1857) and Great Expectations (1861), solidified his reputation as a master storyteller. Dickens was not only a novelist but also a passionate advocate for social change.
His works have had a lasting impact on literature and society, inspiring countless adaptations, films, and plays. Dickens’s legacy endures through his insightful social critiques and his ability to craft memorable, multi-dimensional characters.
Charles Dickens Death and Burial
Charles Dickens died on 9th June 1870 at the age of 58 after suffering a stroke. His death came just days after completing his final novel, The Mystery of Edwin Drood. Contrary to his wishes for a private burial, Dickens was laid to rest in Poet’s Corner at Westminster Abbey in London, a fitting tribute to his immense literary contributions.
Major Themes in Dickens Works
Dickens’s works explore a variety of themes that reflect his concerns about society and the human condition. Some of the most prominent themes in his writing include:
- Social injustice: Dickens highlighted the harsh realities of poverty, child labor, and the inequities of the class system.
- The importance of family: Many of his stories focus on the relationships within families and the ways in which family members care for or betray one another.
- Redemption: Dickens often depicted characters who, like Scrooge, undergo dramatic transformations and seek redemption.
- The plight of the poor: Dickens used his writing to shed light on the difficult lives of the poor, advocating for social reforms.
Conclusion
Charles Dickens was a literary giant whose works continue to resonate with readers around the world. From his humble beginnings in Portsmouth to his rise as one of the most famous novelists of the Victorian era, Dickens’s life and work left a lasting legacy. Through his vivid characters, compelling narratives, and social critiques, Dickens not only entertained but also contributed to meaningful societal change. His stories remain as relevant today as they were when first published, ensuring his place in literary history for generations to come.
1. When did Charles Dickens die?
Charles Dickens passed away on June 9, 1870, at his home, Gads Hill Place.
2. What caused Charles Dickens’s death?
Dickens died from a stroke, which he suffered on June 8, 1870, after a full day’s work on Edwin Drood.
3. Where is Charles Dickens buried?
Despite his wish to be buried privately at Rochester Cathedral, Dickens was laid to rest in Poets’ Corner at Westminster Abbey.
4. What is The Empty Chair illustration?
The Empty Chair is an engraving by Samuel Luke Fildes that depicts the empty chair of Dickens in his study at Gads Hill Place after his death. It was published in The Graphic in 1870.
5. Was Dickens’s death kept private?
Biographer Claire Tomalin suggested that Dickens’s mistress, Ellen Ternan, had him moved back to Gads Hill Place to keep the public unaware of their relationship.
READ MORE :- Singer Frank Ocean Biography, Family, Networth, Career Etc.